Combating, recognizing and preventing clothes moths
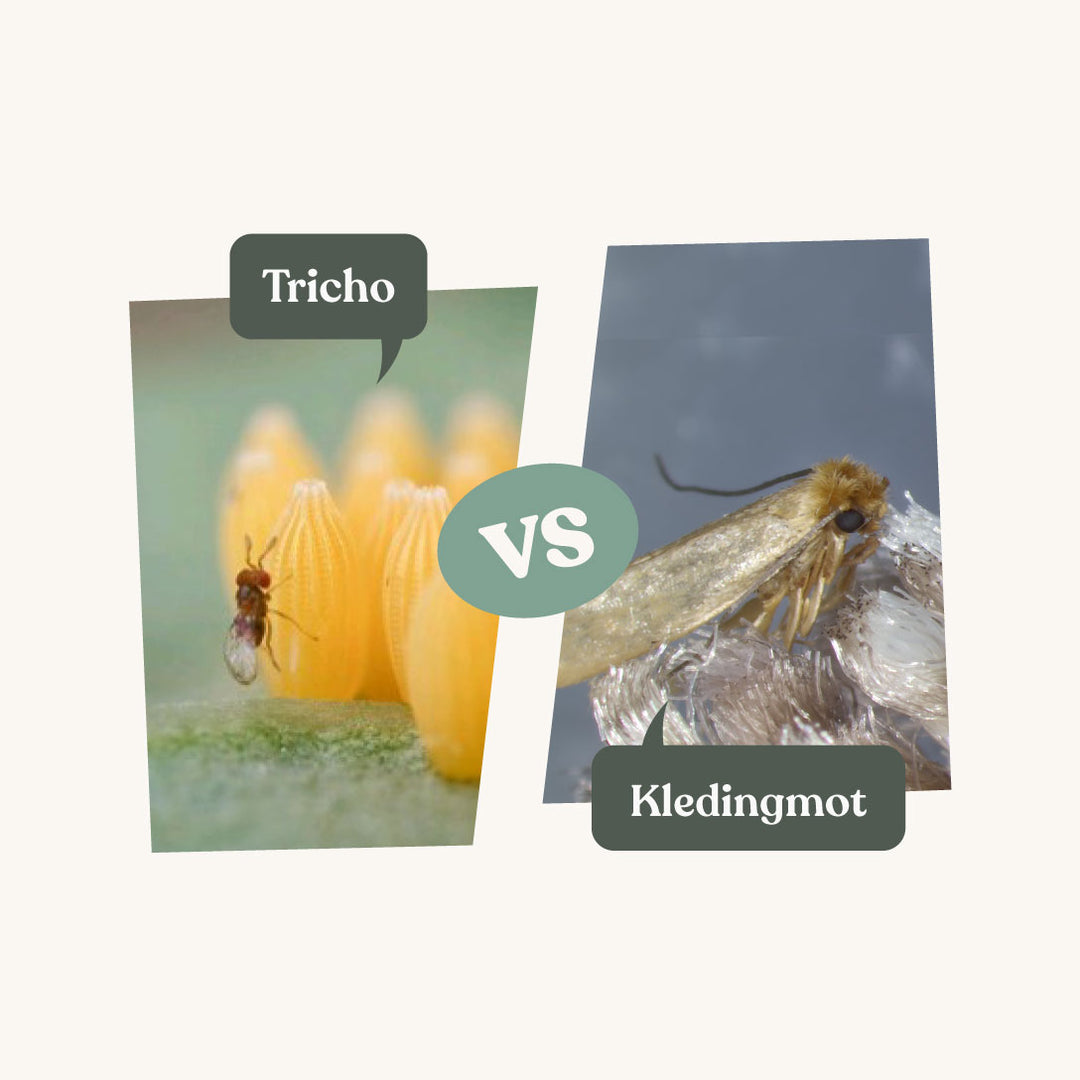
Kledingmot herkennen
De kledingmot (Tineola bisselliella), ook wel klerenmot of kleermot genoemd, is een nachtvlinder die algemeen in Nederland voorkomt. Van nature leeft de kledingmot buiten in oude vogel-, wespen- en zoogdierennesten. De kledingmot komt ook in huis voor, en de rups eet dan van stoffen zoals katoen, zijde, linnen of wol.
De volwassen kledingmotten zich lichtbruin tot lichtgrijs van kleur en ongeveer 10 mm groot. Je zult ze tegenkomen in je kledingkast of bij het tapijt, waar ze opvliegen of wegkruipen als je aan het schoonmaken bent. De volwassen motten brengen geen schade toe, de larven daarentegen wel.
De larven van kledingmotten zijn crème van kleur met een bruine kop. Ze zijn tot 9 mm groot en met het blote oog te zien. De larven knagen aan stoffen waardoor er gaatjes in je kleding, gordijnen of tapijt kunnen ontstaan.
Kledingmot ontwikkeling
De levenscyclus van een kledingmot (Tineola bisselliella) speelt zich af in vier fasen: ei, larve, pop en volwassen mot.
Eistadium
De levenscyclus van de kledingmot begint wanneer het vrouwtje haar eieren legt. Een volwassen kledingmot kan tot 100 eieren leggen, meestal in donkere en rustige omgevingen waar geschikte voedselbronnen zoals wol, zijde, en andere natuurlijke vezels aanwezig zijn. De eieren zijn klein, wit en bijna onzichtbaar voor het blote oog. Na ongeveer vier tot tien dagen komen de eieren uit.
Larvestadium
De larven, die uit de eieren komen, vormen de meest schadelijke fase in de levenscyclus van de kledingmot. De larven voeden zich met keratine, een eiwit dat aanwezig is in natuurlijke vezels zoals wol, haar, en veren. Gedurende dit stadium veroorzaken de larven de bekende schade aan textielproducten. De larvenfase kan tussen één maand tot twee jaar duren.
Popstadium
Na de larvenfase verpopt de kledingmot zich. Tijdens het popstadium omhult de larve zich in een zijden cocon, vaak met kleine deeltjes van het materiaal waarop ze zich hebben gevoed. Dit stadium duurt meestal één tot vier weken.
Volwassen stadium
De volwassen kledingmot verschijnt uiteindelijk uit de cocon. Volwassen motten leven meestal niet langer dan 15 tot 30 dagen en voeden zich niet meer. Hun belangrijkste doel in dit stadium is voortplanting. De vrouwtjes paren en leggen nieuwe eieren, waardoor de cyclus opnieuw begint.
De duur van de volledige levenscyclus van de kledingmot varieert sterk afhankelijk van de omgevingsomstandigheden, maar kan onder gunstige omstandigheden ongeveer 2 tot 3 maanden duren.
Kledingmot schade
Schade van de kledingmot herken je aan kleine, onregelmatige gaatjes in kleding en andere textiel, vooral in materialen zoals wol, zijde, en bont. Deze schade wordt veroorzaakt door de larven van de kledingmot, die zich voeden met keratine, een eiwit dat in dierlijke vezels voorkomt. Naast de gaatjes kun je ook zijdeachtige spinsels, uitwerpselen, en eventueel vervellingshuidjes aantreffen, die de larven achterlaten. De volwassen motten zelf veroorzaken geen schade; het zijn de larven die, door hun vraatzucht, kleding en textiel aantasten, vaak op donkere en rustige plekken zoals in kasten of op tapijten.
Kledingmot bestrijden op natuurlijke wijze
In dit stappenplan leer je hoe je met behulp van Tricho sluipwespen en de Delta trap met lokstof de strijd tegen kledingmotten kunt aangaan.
Stap 1: Stofzuigen en luchten
Voordat je begint met het inzetten van Tricho sluipwespen en Delta vallen, is het essentieel om je ruimte grondig schoon te maken. Stofzuig alle kasten, tapijten, en vloeren waar motten hun eitjes kunnen hebben gelegd. Besteed extra aandacht aan donkere, moeilijk bereikbare plekken zoals achter kasten en onder meubels. Na het stofzuigen is het raadzaam om de kamer goed te luchten. Motten houden van warme, donkere omgevingen, dus door de ruimte te luchten en te verfrissen, maak je de omgeving minder aantrekkelijk voor hen. Berg kleding die je niet vaak draagt in goed afgesloten zakken of dozen op.
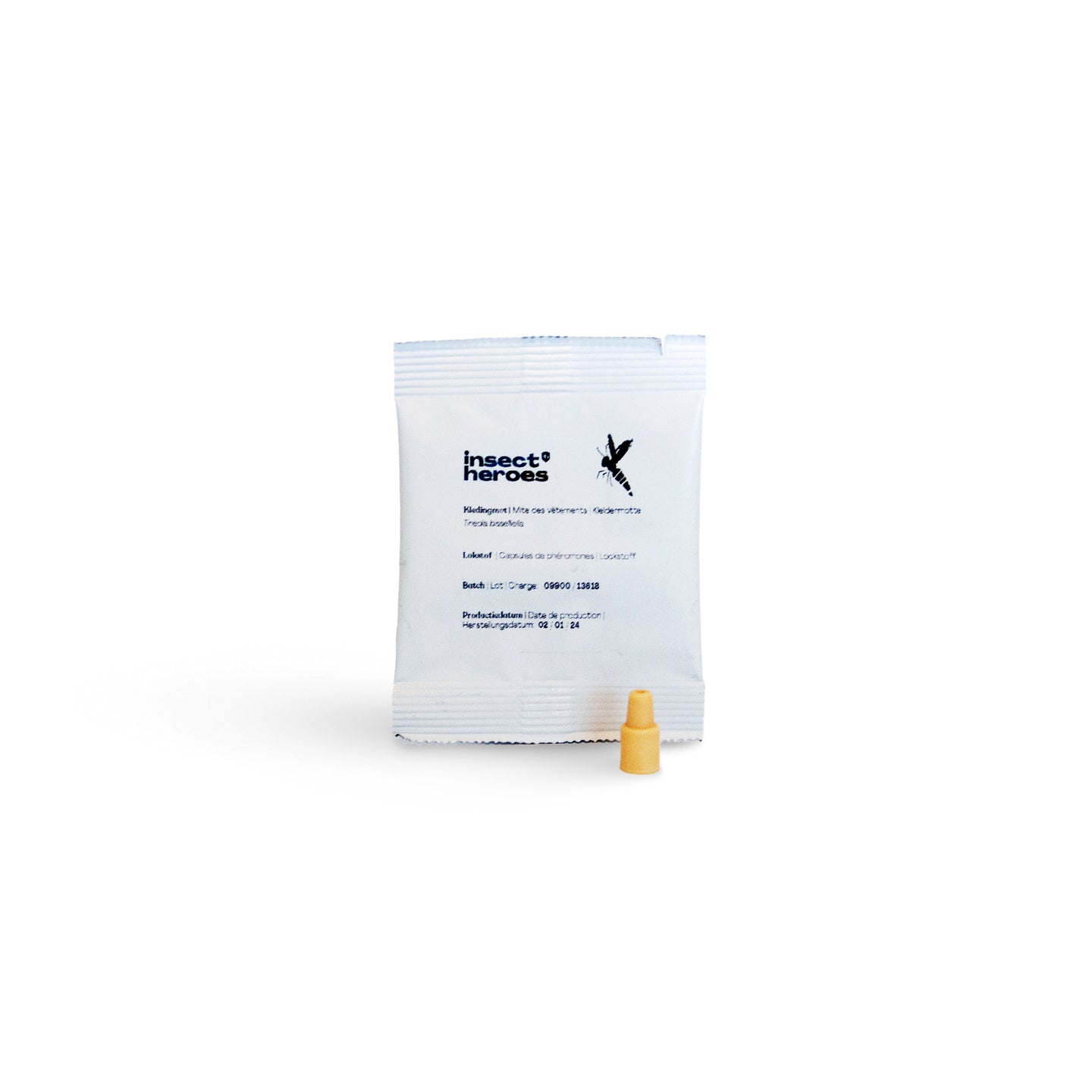
Stap 2: Uitzetten van Tricho sluipwespen
Na het reinigen van de ruimte kun je beginnen met het uitzetten van Tricho sluipwespen. Deze natuurlijke vijanden van de kledingmot parasiteren op de eieren van de motten, waardoor nieuwe larven zich niet kunnen ontwikkelen. Plaats de zakjes met sluipwespen op strategische plekken in je kast of op andere locaties waar je kleding bewaart. Het zakje hoeft niet opengeknipt te worden.
De sluipwespen zullen geleidelijk uit gaatjes in de zakjes kruipen, in een periode tussen de 2-4 weken. Het zakje is zo ontwikkeld dat er 2000 sluipwespen per week uit het zakje komen. Het duurt meestal 2-3 dagen voordat de eerste volwassen sluipwespen uit het zakje komen.
Stap 3: Plaatsen van de Delta Trap val met lokstof
Naast het inzetten van sluipwespen, is het gebruik van de Delta trap val met lokstof een zeer effectieve methode om volwassen motten te vangen. Deze vallen trekken mannelijke motten aan, waardoor de paringscyclus wordt doorbroken. Plaats de vallen in de buurt van de besmette gebieden, zoals kasten en opslagruimtes voor kleding, maar niet direct naast de zakjes sluipwespen. Controleer de vallen regelmatig en vervang de lokstof indien nodig om de effectiviteit te behouden.
Stap 4: Herhalen
Herhaal de behandeling elke 4 weken totdat de kledingmotten zijn verdwenen.
Tips om kledingmotten te voorkomen
Bewaar kleding in luchtdichte verpakkingen
Een van de beste manieren om kledingmotten te voorkomen, is door je kleding op te bergen in luchtdichte zakken of plastic bakken. Motten kunnen niet door deze barrière heen, waardoor je kleding beschermd blijft tegen schade. Dit is vooral belangrijk voor kledingstukken die je niet vaak draagt, zoals winterjassen en wollen truien.
Regelmatig luchten en schoonmaken
Kledingmotten houden van donkere, stille plekken. Door je kleding regelmatig te luchten en je kasten schoon te houden, maak je de omgeving minder aantrekkelijk voor motten. Stofzuig regelmatig in en rond je kledingkasten en vergeet niet om ook onder meubels en in hoeken te reinigen waar stof zich kan ophopen.
Gebruik natuurlijke afweermiddelen
Essentiële oliën zoals lavendel-, ceder- en pepermuntolie kunnen helpen om kledingmotten af te schrikken. Plaats een paar druppels van deze oliën op katoenen balletjes of gebruik geurende zakjes en leg deze in je kasten en laden. Deze oliën hebben niet alleen een afwerende werking, maar geven je kleding ook een aangename geur.
Preventief inzetten van sluipwespen
Het preventief inzetten van Tricho sluipwespen is een zeer effectieve manier om te voorkomen dat kledingmotten zich kunnen voortplanten. Deze sluipwespen parasiteren op de eieren van de motten, waardoor nieuwe mottenlarven zich niet kunnen ontwikkelen. Door deze sluipwespen preventief in te zetten, kun je een eventuele mottenplaag al in de kiem smoren.
Inspecteer tweedehands kleding en textiel
Als je tweedehands kleding of textiel koopt, inspecteer deze dan grondig voordat je ze in je kast hangt. Motten en hun eitjes kunnen zich gemakkelijk verbergen in gebruikte kledingstukken. Door nieuwe aankopen te wassen en te inspecteren, voorkom je dat je onbewust motten in huis haalt.
Andere manieren om kledingmotten te bestrijden
Was kleding op hoge temperatuur
Het wassen van kleding op een hoge temperatuur is een eenvoudige en effectieve methode om kledingmotten te bestrijden. De hitte doodt motten, larven en eitjes. Was besmette kledingstukken op minimaal 60 graden Celsius om ervoor te zorgen dat alle stadia van de mot worden geëlimineerd. Pas op! Niet alle kleding kan op 60 graden Celsius gewassen worden. Delicate materialen zoals zijde, wol en sommige synthetische stoffen kunnen krimpen, vervormen of kleur verliezen.
Invriezen van besmette kleding
Invriezen is een andere effectieve methode om motten en hun larven te doden. Plaats besmette kleding in een plastic zak en laat deze gedurende minimaal 72 uur in de vriezer liggen. De lage temperatuur zal de motten in alle stadia van hun levenscyclus doden. Zorg ervoor dat je de kleding daarna goed laat ontdooien voordat je deze weer opbergt.
Gebruik van mottenspray
Er zijn verschillende commerciële mottensprays beschikbaar die kledingmotten en hun larven doden. Het gebruik van een mottenspray wordt vaak afgeraden vanwege de mogelijke negatieve effecten op zowel het milieu als de persoonlijke gezondheid. Veel mottensprays bevatten synthetische chemicaliën en insecticiden die schadelijk kunnen zijn voor het milieu wanneer ze in de lucht, water of bodem terechtkomen. Bovendien kunnen deze sprays bij inademing of contact met de huid allergische reacties, ademhalingsproblemen of andere gezondheidsklachten veroorzaken, vooral bij mensen met een gevoelige huid, astma of allergieën. Natuurlijke of niet-chemische bestrijdingsmethoden zijn daarom vaak een veiliger en milieuvriendelijker alternatief.
Weet je niet zeker van welke plaag je last hebt?
Bekijk de overzichtspagina met alle plagen.